Synthetic Fibres and Plastics
Handout
Chapter – 3
VIII Grade
Based on NCERT – CBSE Curriculum
Handout Prepared by
Param’s Magazine (www.paramsmagazine.com)
Notes – Synthetic Fibres and Plastics – Chapter – 3 – NCERT – CBSE – Class VIII
Fabrics
- Fabrics are made from fibres
- Sources of fibres:
- Natural Fibres
- Plants
- Animals
- Artificial Fibres (Man-made) – known as Synthetic fibres
- Natural Fibres
Natural Fibres (Plants)
- Cotton (Source: Cotton plant)
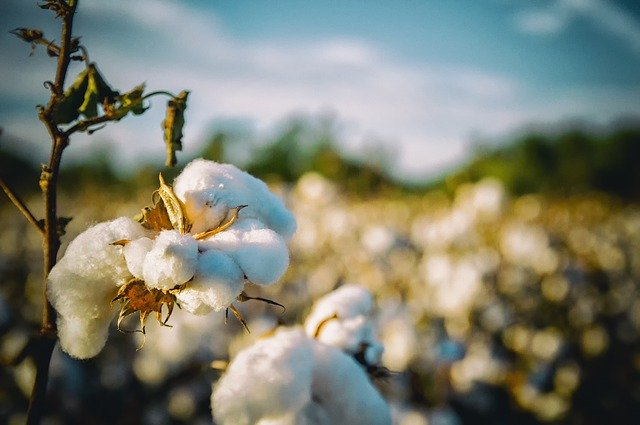

- Jute (Source: Jute plant)
Natural Fibres (Animals)
- Wool (Sources: Sheep, Goat, Camel, Yak, Angora Goat, Llama, Alpaca)
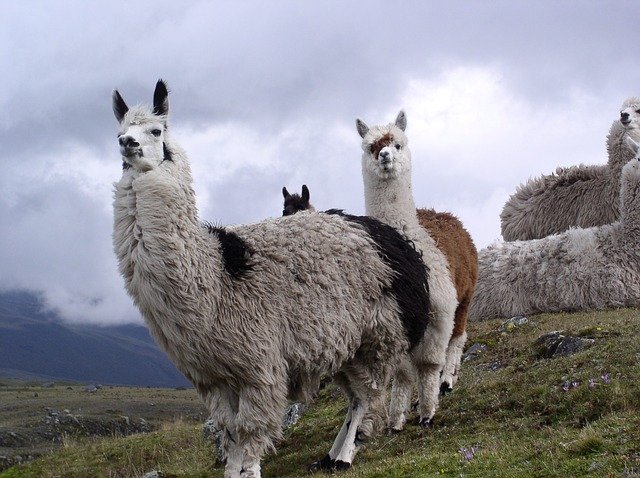

Llama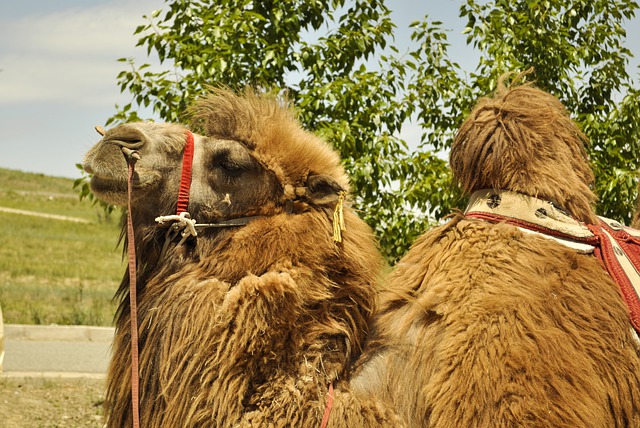 
Camel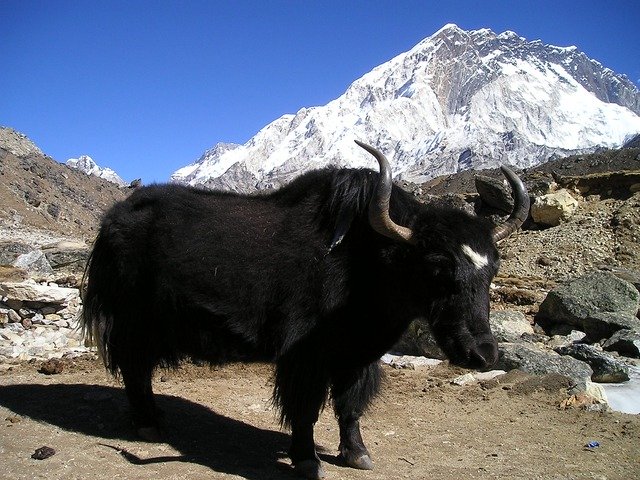 
Yak 
Angora Goat 
Alpaca 
Sheep
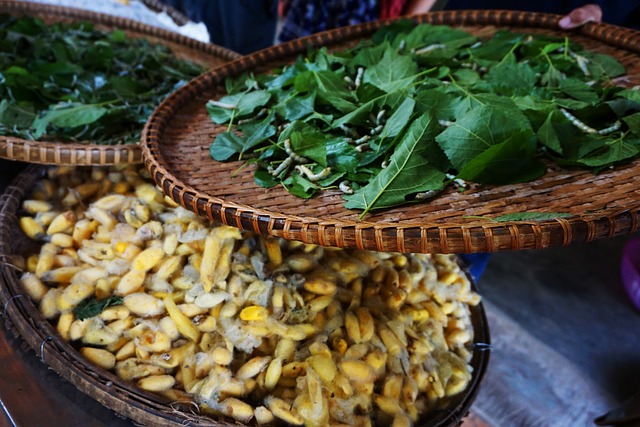
- Silk (Source: Silk worm)

Synthetic Fibres
The structure of synthetic fibre is similar to that of beads connected to the necklace.
- Synthetic fibre is a chain of small units (like the beads in the necklace).
- Each small unit is a chemical substance.
- These small units combine to form a large single unit called Polymer.
Polymer
- “Poly” = Many
- “Mer” = Part / Unit
- Polymer ⇒ Made of many repeating units

Cotton is a natural polymer. It is called cellulose and is made up of a large number of glucose units.
Types of Synthetic Fibres
- Rayon
- Nylon
- Polyester
- Acrylic
Rayon (Artificial Silk)
- Made from wood pulp (natural source)
- The fibre is obtained by chemical treatment of the wood pulp.
- Although rayon is made from the natural source (wood pulp), it is man-made.
- Cheaper than silk
- Can be woven like silk fibres
- Can be dyed in a variety of colors
- Rayon is mixed with cotton to make bedsheets
- Rayon is mixed with wool to make carpets
Nylon
- Nylon is the first, fully synthetic fibre
- Made without any natural raw materials from plant or animal
- Made from coal, water and air
- Properties:
- Strong, elastic and light. Stronger than steel wire
- Lustrous and easy to wash
- Articles made from nylon:
- Socks, ropes, tents, toothbrushes, car seat belts, sleeping bags, curtains, etc
- Parachutes
- Ropes for rock climbing
Polyester
- Synthetic fibre
- Does not get wrinkled easily
- Remains crisp (stiff and smooth) and easy to wash
- Suitable for making dress materials like polyester shirts and dresses.
- Polyester = Poly + Ester ⇒ Made of repeating units of chemical called ‘ester’.
- Esters give fruits their smell.
- Polyester fabrics:
- Polycot (Mixture of polyester and cotton)
- Polywool (Mixture of polyester and wool)
- Terrycot (Mixture of terylene and cotton)
- Terylene
- Terylene is a popular polyester
- It can be drawn into very fine fibres, which can be woven like any other yarn.
- PET (polyethylene terephthalate)
- PET is a familiar form of polyester
- It is used for making bottles, utensils, films, wires, etc
Acrylic
- Artificial wool
- Cheaper than wool obtained from natural sources
- Available in variety of colors
- More durable and affordable than natural fibres
- Used to make sweaters, shawls and blankets

All the synthetic fibres are prepared by a number of processes using raw materials of petroleum origin, called petrochemicals.
Characteristics of Synthetic Fibres
- They dry up quickly
- are durable
- less expensive
- readily available and
- easy to maintain
Disadvantage of Synthetic Fibres
- Synthetic fibres melt on heating. They can easily catch fire. If the clothes catch fire, the fabric melts and sticks to the body. One should avoid wearing synthetic clothes while working in laboratories or kitchen.
Plastics
- Plastic is a polymer like synthetic fibre
- Plastics have two different types of arrangements (Linear and Cross-linked)
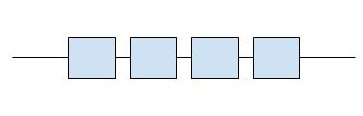
Linear Arrangement of Polymer in Plastic
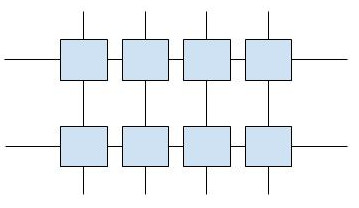
Cross-linked Arrangement of Polymer in Plastic
- Plastics are available in all possible shapes and sizes
- Easily mouldable
- Can be recycled, reused, colored, melted, rolled into sheets or made into wires.
Types of Plastics
- Thermoplastics
- Thermosetting Plastics
Thermoplastics
- Can be deformed on heating
- Can be bent easily
- Types:
- Polythene
- PVC (Polyvinyl chloride)
Polythene
- (Poly+ethene) is an example of a plastic. It is used for making commonly used polythene bags.

Polythene Bag 
PVC Electrical Wire
Thermosetting plastics
- When moulded once, can not be softened by heating
- Types:
- Bakelite
- Melamine
Bakelite
- Bakelite is a poor conductor of heat and electricity.
- It is used for making electrical switches, handles of various utensils, etc.
Melamine
- Melamine is a versatile material.
- It resists fire
- It can tolerate heat better than other plastics.
- It is used for making floor tiles, kitchenware and fabrics which resist fire.
Applications of Plastics
- Plastic containers for storing a food items like water, milk, pickles, dry food etc.
- Being lighter as compared to metals, plastics are used in cars, aircrafts and spacecrafts.
- Slippers, furniture, decoration pieces
- Handles of frying pans, plastic covering for electrical wires, handle of screw drivers
- Healthcare Industry
- packaging of tablets, threads used for stitching wounds, syringes, doctors’ gloves and a number of medical instruments.
- Cookware
- Special plastic cookware is used in microwave ovens for cooking food. In microwave ovens, the heat cooks the food but does not affect the plastic vessel.
- Teflon is a special plastic on which oil and water do not stick. It is used for non-stick coating on cookwares.
Advantages of Plastic Materials
- Light weight
- Lower price
- Good strength
- Easy handling
Characteristics of Plastic Materials
- Plastics do not react with water and air
- They are not corroded easily. That is why they are used to store various kinds of material, including many chemicals.
- Very light, strong, durable, can be moulded in to different shapes and sizes
- Cheaper than metals
- Poor conductors of heat and electricity (Applications: Handles of frying pans, plastic covering for electrical wires, handle of screw drivers)
Plastics and the Environment
- Plastic waste gets accumulated due to wide usage of plastic materials or polythene bags. It results in disposal of plastic wastes.
- Plastic is non-biodegradable ⇒ It does not get decomposed by natural processes.

Biodegradable – A material which gets decomposed through natural processes, such as action by bacteria, is called biodegradable.
Problems caused by plastics
- Plastic takes years to decompose
- It is not environment friendly
- It causes environmental pollution
- The burning process in the synthetic material is quite slow and it does not get completely burnt easily. In the process it releases lots of poisonous fumes into the atmosphere causing air pollution.
- When animals eat food wastes, they swallow materials like polythene bags or wrappers. The plastic material chokes the respiratory system or form a lining in their stomach, which may result in the death of the animals.
- Polythene bags thrown carelessly can clog the drains.
Solution to environmental problems caused by plastics
- Avoid the use of plastics as much as possible
- Do not throw plastics into water bodies
- Make use of bags made of cotton or jute
- The biodegradable and non-biodegradable materials should be collected separately and disposed of separately
- Recycle plastic waste
- Follow 5 R principle ⇒ Reduce, Reuse, Recycle, Recover and Refuse










Be the first to comment